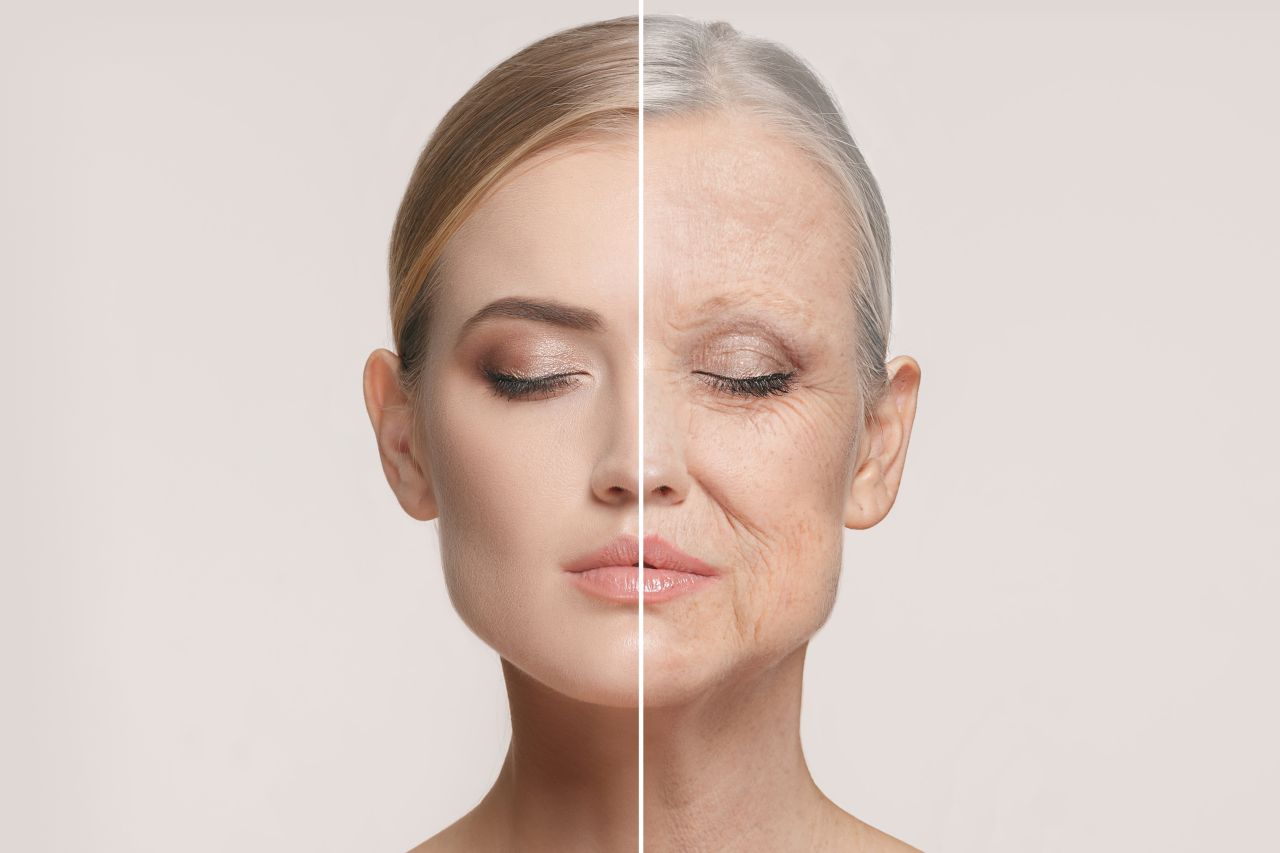
How does stress cause premature aging?
Stress causes premature aging through several biological processes that occur in response to chronic exposure to stressors. The primary mechanisms include:
- Hormonal changes: Chronic stress increases the production of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. High levels of cortisol can damage various cells and organs over time, and can inhibit the production of growth hormones, leading to slower cell renewal and repair, thus contributing to aging.
- Telomere shortening: Telomeres are the protective caps on the ends of chromosomes, and they shorten with each cell division. Shortened telomeres are associated with aging and age-related diseases. Stress has been shown to accelerate telomere shortening, possibly due to increased oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Oxidative stress: Stress can lead to increased production of free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells through a process called oxidative stress. To counteract this damage, our bodies have natural repair mechanisms, but prolonged stress can overwhelm these mechanisms, leading to more extensive cellular damage that is associated with aging.
- Inflammation: Prolonged stress stimulates the immune system, leading to chronic low-grade inflammation, which plays a crucial role in the development of many age-related diseases, including heart disease, arthritis, and neurodegenerative conditions. This ongoing inflammation can damage tissue, accelerate cellular aging, and increase vulnerability to illnesses.
- Lifestyle factors: Stress can lead to unhealthy habits such as poor sleep, physical inactivity, and poor diet, all of which contribute to premature aging by undermining overall health and well-being.
Overall, the physiological responses to stress can interact in complex ways that ultimately lead to cellular damage, maladaptive changes in organ systems, and increased susceptibility to age-related diseases, resulting in accelerated aging.
What Can You Do to Control Stress-Related Skin Aging?
- Identify stressors: Recognize the factors in your life that may be causing stress, such as work, relationships or financial issues, and address them accordingly.
- Practice stress management techniques: Incorporate stress-reducing practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation into your daily routine.
- Get regular exercise: Physical activity has been shown to decrease stress levels and improve overall health, including skin health.
- Eat a balanced diet: A healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats can support skin health and help reduce inflammation associated with premature aging.
- Prioritize sleep: Make sure you are getting adequate rest each night, as poor sleep can contribute to stress and inflammation, worsening skin aging.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help maintain skin’s moisture and support overall health.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine consumption: Excessive alcohol and caffeine intake can dehydrate the skin, increase inflammation and exacerbate stress, which can lead to premature aging.
- Maintain a consistent skincare routine: Regularly cleanse, exfoliate, moisturize, and apply sunscreen to protect your skin from environmental damage and keep it looking youthful.
- Seek professional help if needed: If stress-related skin aging becomes a significant concern, consider seeking the advice of a dermatologist, psychologist or other healthcare professional.
- Stay socially connected: Maintaining strong relationships with friends and loved ones can help reduce stress, improve overall well-being, and support a healthy, youthful appearance.
Other habits that may contribute to premature skin aging
It’s important to note that stress isn’t the only habit you may have that’s causing premature aging of your skin. Here’s a few more:
- Excessive sun exposure: Prolonged and unprotected sun exposure can lead to premature skin aging by causing damage to the skin’s elastin and collagen fibers. This can result in wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots.
- Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients and oxygen. It also damages collagen and elastin fibers, leading to sagging skin and wrinkles.
- Poor diet: A diet low in essential nutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants can negatively impact skin health and contribute to premature aging.
- Lack of sleep: Chronic sleep deprivation can cause an increase in cortisol levels, leading to inflammation and collagen breakdown, resulting in premature skin aging.
- Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can dehydrate the skin, causing it to lose its elasticity and appear dull, tired, and aged.
- Inadequate skincare: Neglecting to cleanse, moisturize, and exfoliate the skin can lead to a buildup of dead skin cells and clogged pores, which can accelerate the aging process.
- Pollution exposure: Prolonged exposure to environmental pollutants such as smog, dust, and chemicals can damage the skin, leading to premature aging.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can lead to dehydrated skin, which can appear dull, flaky, and more prone to fine lines and wrinkles.
- Frequent use of hot water: Using hot water to cleanse the skin can strip it of its natural oils, leading to dryness, irritation, and premature aging.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and taking care of your skin, you can reduce or delay the signs of premature skin aging.
*Information in this article is not medical advice and may not be factually accurate. It is intended for entertainment purposes only. Consult with a physician before attempting any tips in this blog post and to get the most up to date factual data about any procedure or treatment.