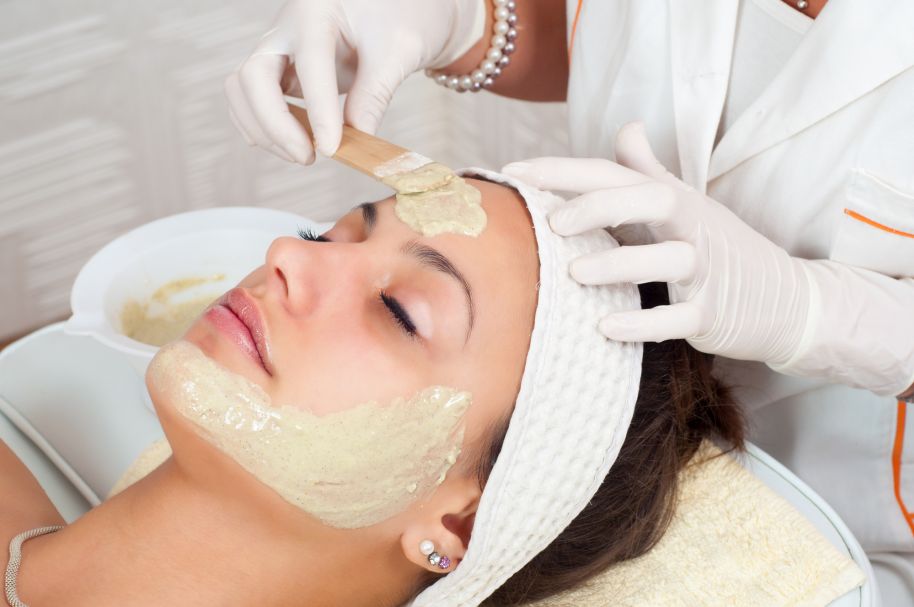
Having smooth and radiant skin is everybody’s skincare goal. Unfortunately, the bridge between you and beautiful skin is often a layer of dead skin cells. Your old skin cells are naturally replaced with new and healthy cells every month. Not all the old or dead cells shed from the surface. Instead, they adhere to the skin or build up in your pores, resulting in a dull and lifeless complexion.
What is Exfoliation and How Does it Work?
Your skin naturally sloughs off dead skin cells, but the process slows down with age. As a result, they appear as dry patches, fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. You can remove the dead skin cells with a physical or chemical exfoliating tool. But it is crucial to consider an exfoliant according to your skin type and doing it properly can lead you to have a brighter and smoother complexion. On the other hand, it can irritate or damage your skin if not done correctly.
Types Of Exfoliants
- Physical Exfoliants- Microbeads, sugar crystals, hard particles, sponges, loofah are types of physical exfoliants. When these scrubbing particles get rubbed on the skin, they remove dead skin cells, increase blood circulation, and give your skin an instant glow.
- Chemical Exfoliants- Alpha hydroxy acids or beta hydroxy acids are chemical exfoliants. They bond with dead skin cells and remove them from the surface. Apart from exfoliation, they lighten hyperpigmentation, and reduce the appearance of pores, wrinkles, and fine lines.
Exfoliate According to Your Skin Type
Considering your skin type is essential while choosing an exfoliant. Here are some recommendations.
Dry Skin
People with dry skin always find it difficult to maintain the moisture barrier. So, if your skin is peeling, dry, or flaky, you should bring up the hydration level before exfoliation. Use a mild exfoliating agent like lactic acid or glycolic acid. Start by doing it once a week and then work your way up to two times a week. Dry skin should avoid harsh physical exfoliants.
Oily Skin
Abrasive physical exfoliants like sugar, salt, or large beads can worsen the condition of acne. On the other hand, chemical exfoliants like salicylic acid or azelaic acid help lighten acne scars, control excess sebum, and improve skin texture. People with oily or acne-prone skin can exfoliate 3-4 times a week.
Normal or Combination Skin
People with normal or combination skin can use both physical and chemical exfoliants. A facial cleanser with alpha-hydroxy acids targets the oil at T-zone and prevents clogging of pores, without irritating. If you want to use a physical exfoliating agent, start using once or twice a week and observe how your skin reacts. If you don’t notice any adverse reaction, you can even use the scrub 3 to 4 times a week to attain a healthy and glowing complexion.
Sensitive Skin
Like dry skin, exfoliating sensitive skin requires you to be very gentle because it becomes inflamed and irritated easily. Lactic acid is the gentlest chemical exfoliant. It has moisturizing and skin softening properties and can be used regularly. Physical scrubbing should be avoided.
Exfoliate Your Lips
Removing dead skin cells from lips is essential to keep them rosy and plump. You can make your own scrub by mixing sugar grains or coffee powder in honey. Massage it in circular motions for 2-3 minutes and wipe it away with a damp washcloth.
Exfoliate Your Body
Like your face, achieving smooth and bright skin on the body requires exfoliation too. You can use a body brush or loofah over your dry skin, working towards the heart. Repeat the process 2-3 times to effectively remove dead skin cells. Using a body scrub while taking a shower is another great idea to get smooth and radiant skin.
*Information in this article is not medical advice and may not be factually accurate. It is intended for entertainment purposes only. Consult with a physician before attempting any tips in this blog post and to get the most up to date factual data about any procedure or treatment.